Table of Contents
Variables can store data of different types, and different data types can do different things.
PHP supports the following data types:
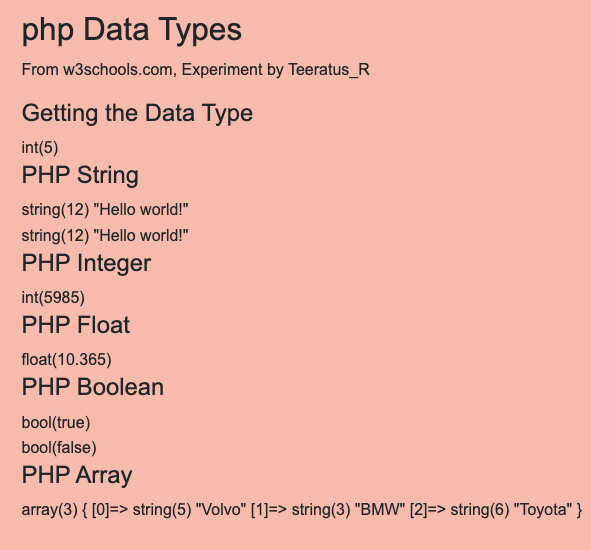
<h2>php Data Types</h2>
<p>From w3schools.com, Experiment by Teeratus_R </p>
<h4>Getting the Data Type</h4>
<?php
// The PHP var_dump() function returns the data type and value:
$x = 5;
var_dump($x);
?>
<h4>PHP String</h4>
<?php
$x = "Hello world!";
$y = 'Hello world!';
var_dump($x);
echo "<br>";
var_dump($y);
?>
<h4>PHP Integer</h4>
<?php
$x = 5985;
var_dump($x);
?>
<h4>PHP Float</h4>
<?php
$x = 10.365;
var_dump($x);
?>
<h4>PHP Boolean</h4>
<?php
$x = true;
$y = false;
var_dump($x);
echo "<br>";
var_dump($y);
?>
<h4>PHP Array</h4>
<?php
$cars = array("Volvo", "BMW", "Toyota");
var_dump($cars);
?>

Result View Example
Classes and objects are the two main aspects of object-oriented programming.
A class is a template for objects, and an object is an instance of a class.
When the individual objects are created, they inherit all the properties and behaviors from the class, but each object will have different values for the properties.
Let's assume we have a class named Car that can have properties like model, color, etc. We can define variables like $model, $color, and so on, to hold the values of these properties.
When the individual objects (Volvo, BMW, Toyota, etc.) are created, they inherit all the properties and behaviors from the class, but each object will have different values for the properties.
If you create a __construct() function, PHP will automatically call this function when you create an object from a class.
<h4>php Object</h4>
<p>From w3schools.com, Experiment by Teeratus_R </p>
<?php
class Car {
public $color;
public $model;
public function __construct($color, $model) {
$this->color = $color;
$this->model = $model;
}
public function message() {
return "My car is a " . $this->color . " " . $this->model . "!";
}
}
$myCar = new Car("red", "Volvo");
var_dump($myCar);
?>

Result View Example
Null is a special data type which can have only one value: NULL.
A variable of data type NULL is a variable that has no value assigned to it.
Tip: If a variable is created without a value, it is automatically assigned a value of NULL.
Variables can also be emptied by setting the value to NULL:
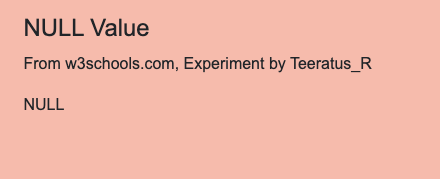
<h4>NULL Value</h4>
<p>From w3schools.com, Experiment by Teeratus_R </p>
<?php
$x = "Hello world!";
$x = null;
var_dump($x);
?>
Result View Example
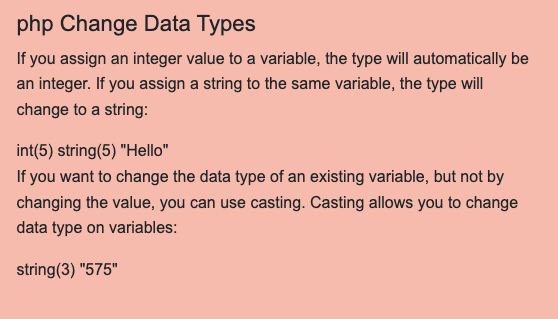
<h4>php Change Data Types</h4>
<p>If you assign an integer value to a variable, the type will automatically be an integer.
If you assign a string to the same variable, the type will change to a string:</p>
<?php
$x = 5;
var_dump($x);
$x = "Hello";
var_dump($x);
?>
<p>If you want to change the data type of an existing variable, but not by changing the value, you can use casting.
Casting allows you to change data type on variables:</p>
<?php
$x = 575;
$x = (string) $x;
var_dump($x);
?>
Result View Example
The special resource type is not an actual data type. It is the storing of a reference to functions and resources external to PHP.
A common example of using the resource data type is a database call.
We will not talk about the resource type here, since it is an advanced topic.
Document in project
You can [Download PDF](php-Data _Types.pdf) file.